电量分析法薄膜透氧性测试标准概要 ——ASTM D 3985
YBB00082003 中对电量分析法的介绍相对较少,现结合 YBB00082003 的参照标准 ASTM D 3985 进行详细介绍。
1、适用范围
This test method covers a procedure for determination of the steady-state rate of transmission of oxygen gas through plastics in the form of film, sheeting, laminates, coextrusions, or plastic-coated papers or fabrics. [1] (本测试方法探讨了一种用于确定氧气渗透通过某些塑料的稳定渗透速率的测试方法,包括薄膜、薄片、层压膜、挤出膜、涂塑纸张或织物。)本标准仅用于检测试样在干燥状态(相对湿度在 1% RH 以下)的透氧性,在潮湿状态下进行检测可参见 ASTM F 1927,多数薄膜的透氧性会随着湿度的变化出现显著差异。
2、测试方法概要
The specimen is mounted as a sealed semi-barrier between two chambers at ambient atmospheric pressure. One chamber is slowly purged by a stream of nitrogen and the other chamber contains oxygen. As oxygen gas permeates through the film into the nitrogen carrier gas, it is transported to the coulometric detector where it produces an electrical current, the magnitude of which is proportional to the amount of oxygen flowing into the detector per unit time. [1] (试样作为密封的半阻隔物,在环境大气压下装夹于两测试腔之间。一腔被氮气流缓慢净化,另一腔 充有氧气。当氧气渗透通过薄膜进入载气氮气流中,它会被载气流携带至库仑传感器处,库仑传感器探测到氧气会输出电流,电流的大小与单位时间内流入传感器的氧气总量成比例。)其中氧气为测试气体,氮气 为载气气体,上腔为氧浓度高的一侧,而下腔为氧浓度低的一侧(可参见图 1),这样就在试样两侧形成一定的氧浓度差,在整个渗透过程中氧气从上腔透过试样向下腔渗透。
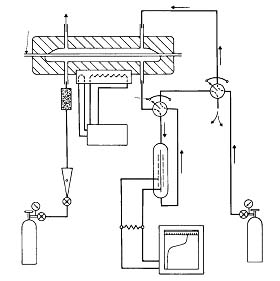
图 1. 电量分析法设备原理图
3、测试干扰
The presence of certain interfering substances in the carrier gas stream may give rise to unwanted electrical outputs and error factors. Interfering substances include free chlorine and some strong oxidizing agents. Exposure to carbon dioxide should also be minimized to avoid damage to the sensor through reaction with the potassium hydroxide electrolyte. [1] (当载气流中存在某些干扰介质时可能会使输出电信号增大,并增加误差因素。干扰物质包括游离氯以及一些强氧化剂。应尽量减少暴露在二氧化碳中,因为与氢氧化钾电解液的反应会对传感器产生损害。)
4、设备的标定
The oxygen sensor used in this test method is a coulometric device that yields a linear output as predicted by Faraday's Law. In principle, four electrons are produced by the sensor for each molecule of oxygen that passes into it. Experience has shown… under some circumstances the sensor may become depleted or damaged to the extent that efficiency and response are impaired. For that reason, this test method incorporates means for a periodic sensor evaluation. [1] (本测试方法中所使用的氧气传感器是一种按照法拉第定律产生线性输出的库仑装置。在原理上,每个进入传感器的氧分子可以使得传感器输出 4 个电子。经验表明…在一些情况下会由于传感器损耗、损坏达到一定程度而削弱传感器的响应效率。因此,在本试验方法中写入了传感器的周期评估方法。)标定设备时需要使用标准膜,由于标准膜的数据能够直接影响到标定系数 Q 的测定,因此需要特别注意标准膜的准备以及标定试验的重复性。本标准中使用 NIST 标准材料进行标定测试。
5、试验过程
Preparation of apparatus… Heating the apparatus will speed the drying and outgassing process… Inserting the specimen… Purging the system… purge air from the upper and lower diffusion cell chambers, using a flow rate of 50 to 60 mL. After 3 or 4 min, reduce the flow rate to the desired value between 5 and 15 mL/min. Maintain this configuration for 30min… INSERT THE SENSOR so that the carrier gas which has passed through both sides of the diffusion cell is diverted into the sensor… Establish E 0 … Switch OXYGEN into the test-gas side of the diffusion cell… The sensor output current should increase gradually, ultimately stabilizing at a constant value. While some thin films with high diffusion coefficients may reach equilibrium in 30 to 60 min, thicker or more complex structures may require a number of hours to reach a steady state of gas transmission. The steady-state voltage value of the oxygen transmission rate shall be recorded and labelled E e . [1] (准备设备。…对设备进行加热可加速干燥过程以及脱气过程。…插入试样。…吹扫系统…用 50 ~ 60mL 的氮气流净化上下腔内的空气。3、4 分钟后将氮气流流速降至 5 ~ 15mL/min 内某一理想流速。保持这种配置 30 分钟。…将设备调至 INSERT THE SENSOR 状态,这样就可以将流经上下腔中的载气气流引入传感器。…确定 E 0。…将扩散腔中试验气体一侧调至 OXYGEN 状态。…传感器输出电流将逐渐增大,最终稳定在一恒定值上。对于较薄且扩散系数大的薄膜达到渗透平衡可能仅需 30 ~ 60 分钟,但对较厚且结构复杂的薄膜要达到稳定渗透的状态可能需要数小时。记录氧气渗透稳定时的电压值,并将它标为 E e。)在整个试验过程中,载气流的流速是否合适是至关重要的,必须按照标准精确调节。
试验结束后,可按照标准中给出的公式由试验中得到的 E 0 和 E e 计算得出试样的氧气透过系数。
6、其它注意事项
首先,采用的氧气传感器是消耗型传感器,当传感器的输出信号出现了明显的衰减且无法通过标定系统来弥补时就需要更换传感器。Back diffusion of air into the unit is undesirable. [1] (最好不要出现空气反向渗透进入系统的情况。)因为空气中的氧会消耗传感器,缩短其使用时间。
其次, High oxygen concentrations in the carrier gas, from the testing of poor barriers, will tend to produce detector saturation. [1] (测试低阻隔性试样时,载气流中的氧含量高,这将使传感器趋于饱和。)这样会缩短传感器的使用时间。有两个方法可以解决这个问题,一种是将氧气和氮气混合以降低测试气体中的氧气含量(测试时试样两侧的氧浓度差降低),另一种是用胶粘剂或环氧树脂将由薄金属片或铝箔制成的遮挡板粘贴在试样两侧以减少试样的面积,这时试样面积等于遮挡板上的开口面积。
再次,需要控制测试温度。Temperature is a critical parameter affecting the measurement of O2 GTR. [1] (温度是影响试样氧气透过性测试的关键参数。)严格控温可以减小由于温度波动给测试结果带来的影响。
7、总结
ASTM D 3985 是目前使用氧传感器检测薄膜透氧性的常用标准,也是 YBB00082003 中电量分析法的参照标准,对于这条标准的深入理解将有助于更好地执行 YBB00082003。温度和湿度是影响最终试验数据的关键参数,因此对试验环境进行有效控制是提高试验精度及效率的有效手段。
文章地址:http://service.labthink.cn/cn/article-Permeation-info-11011840.html
版权所有 Labthink兰光 未经许可禁止转载 转载请注明出处

